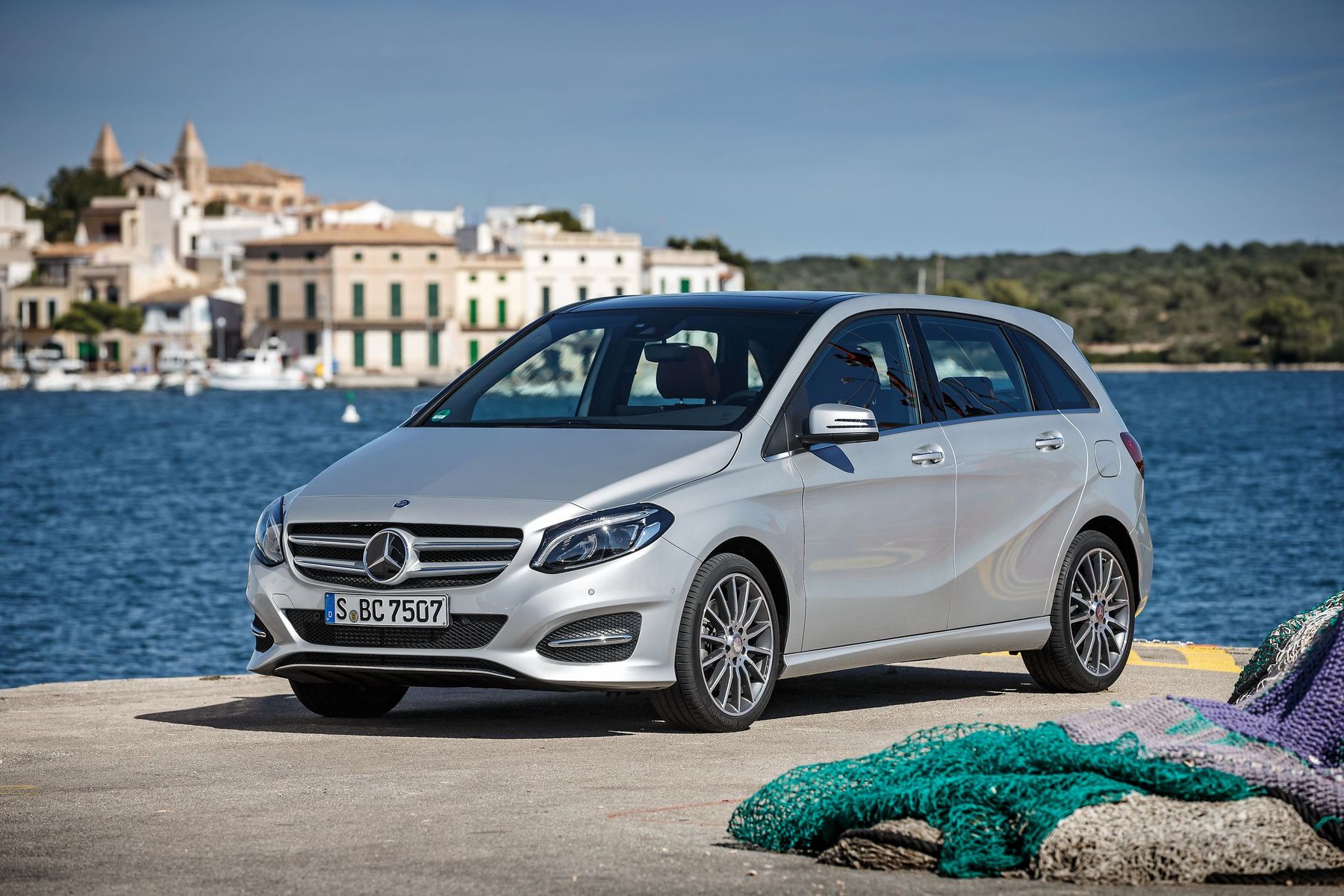
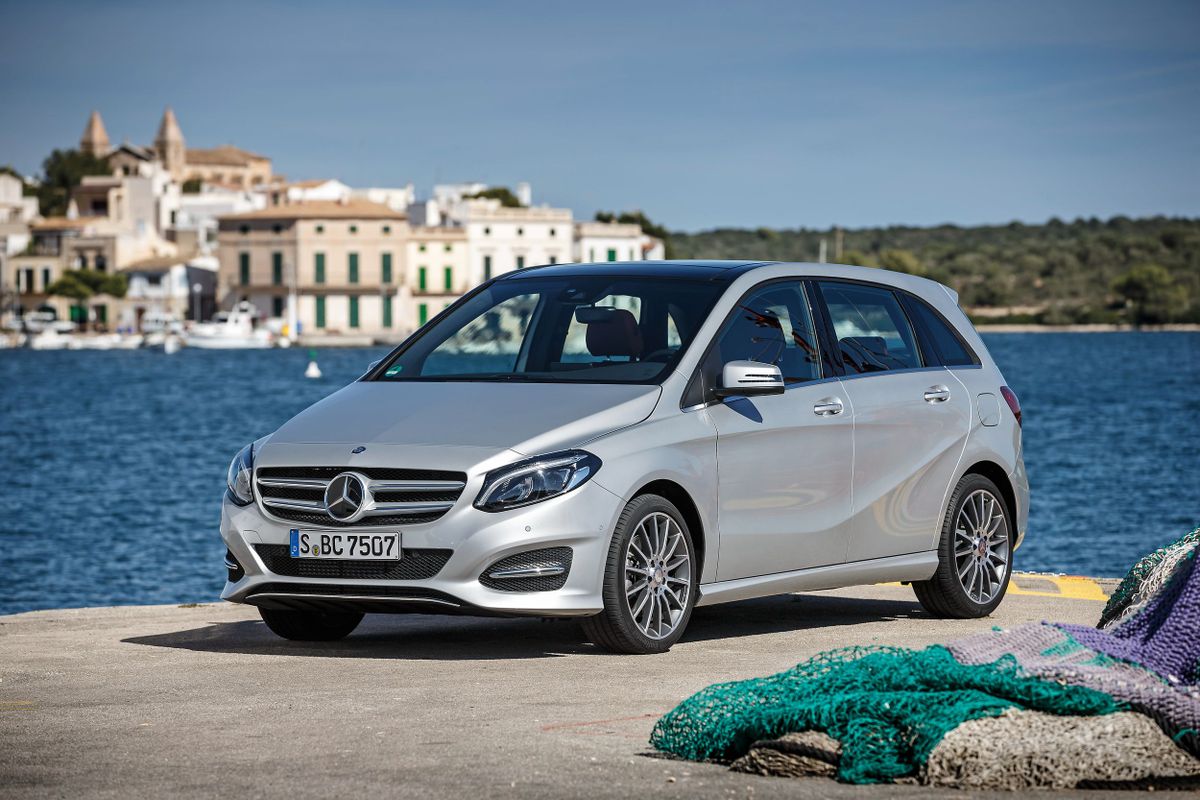
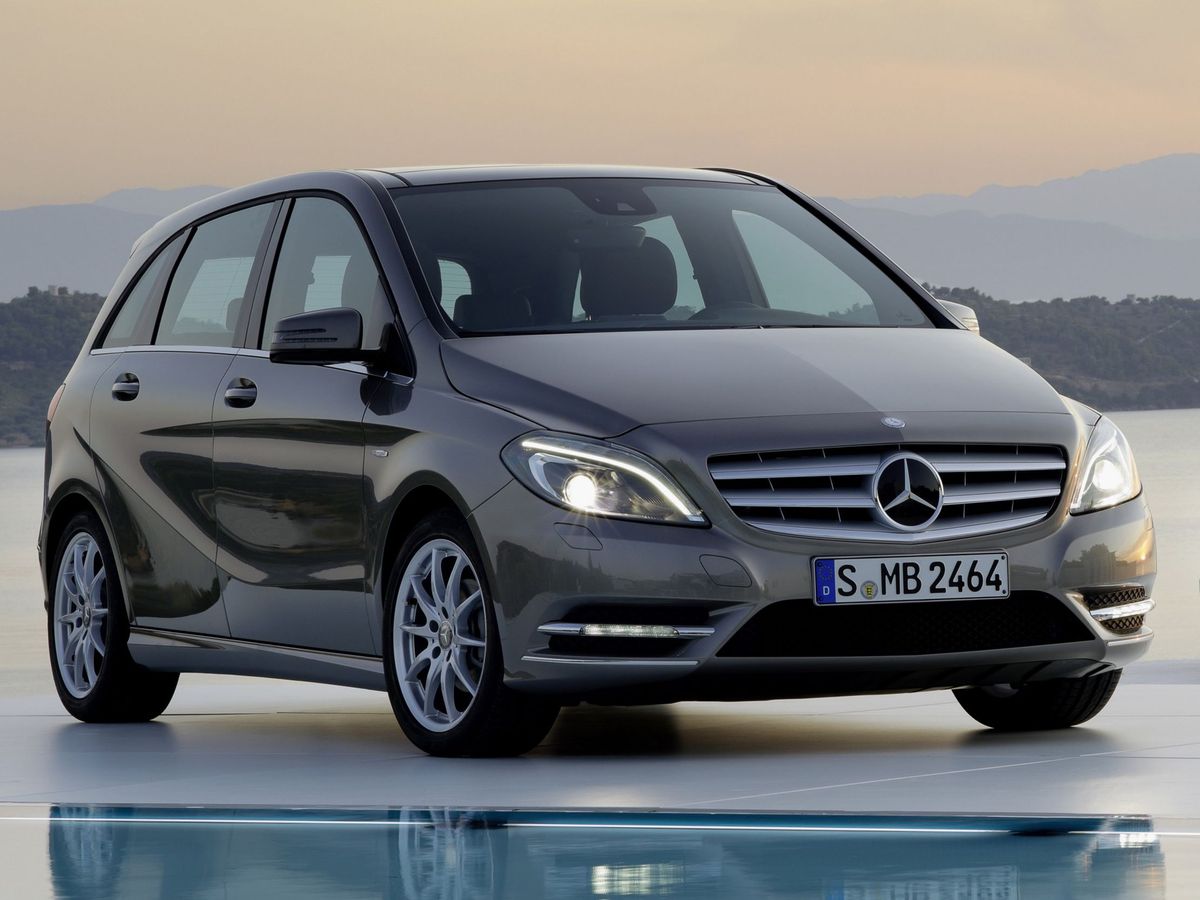
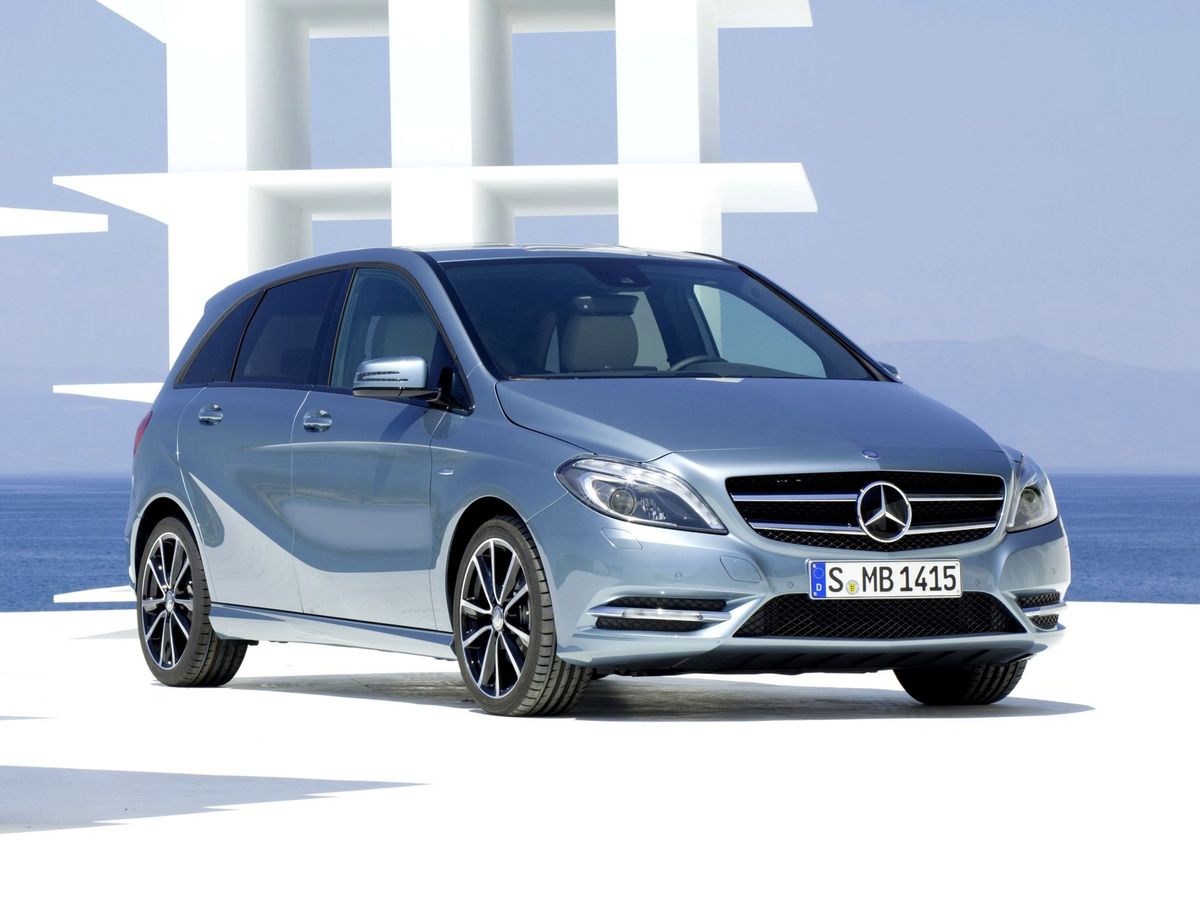
Perfect space in the most attractive guise
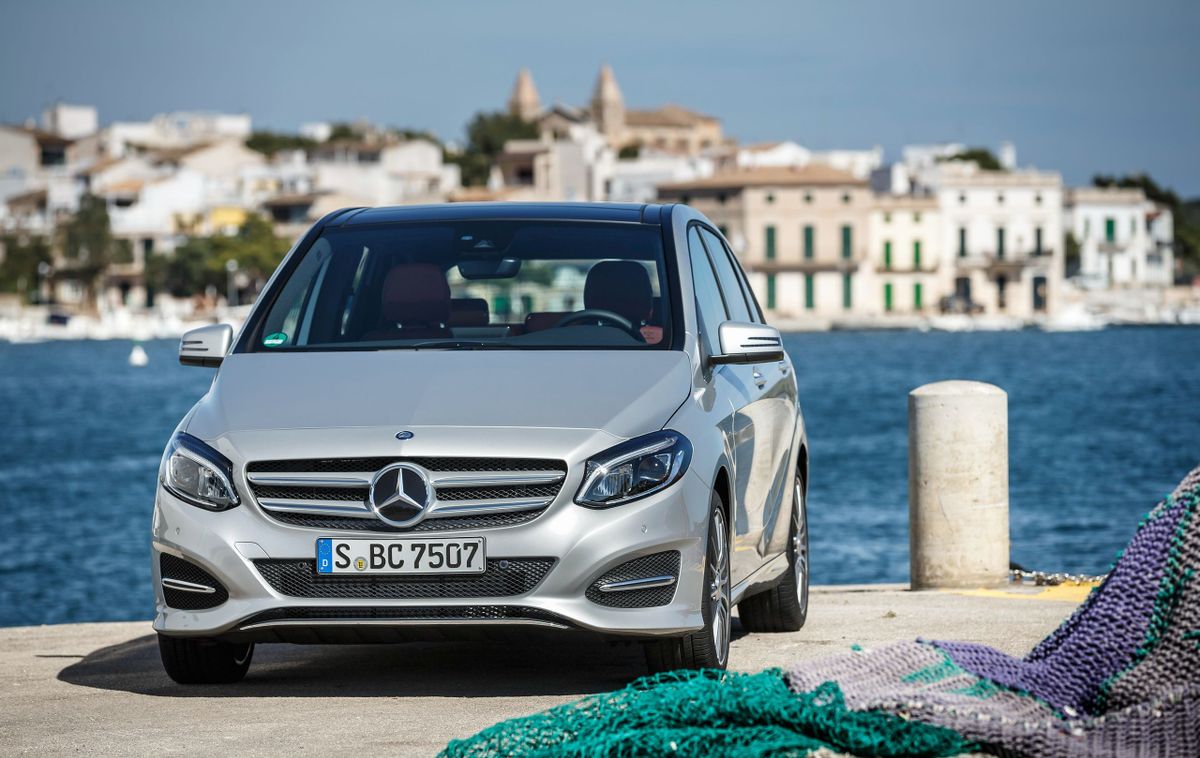
The second generation of the Mercedes B-Class was produced from 2011 to 2018, and was restyled in 2014. The first generation underwent a major overhaul to spark the fading interest in the vehicle, which occupies an intermediate position between the compact car and the minivan. When creating the second generation, the developers were primarily focused on the vehicle design. ‘Perfect space in the most attractive guise’ was a slogan that accompanied the design.
Dynamic design
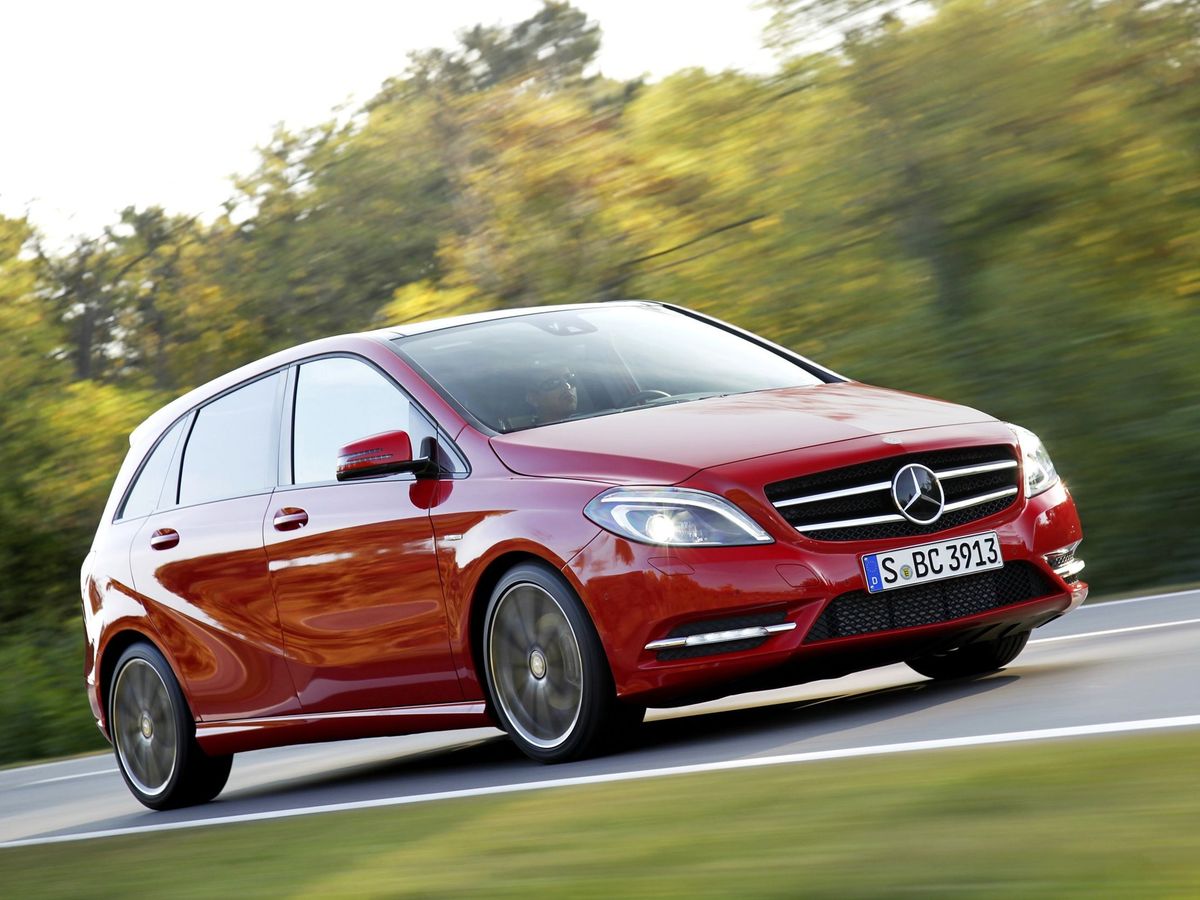
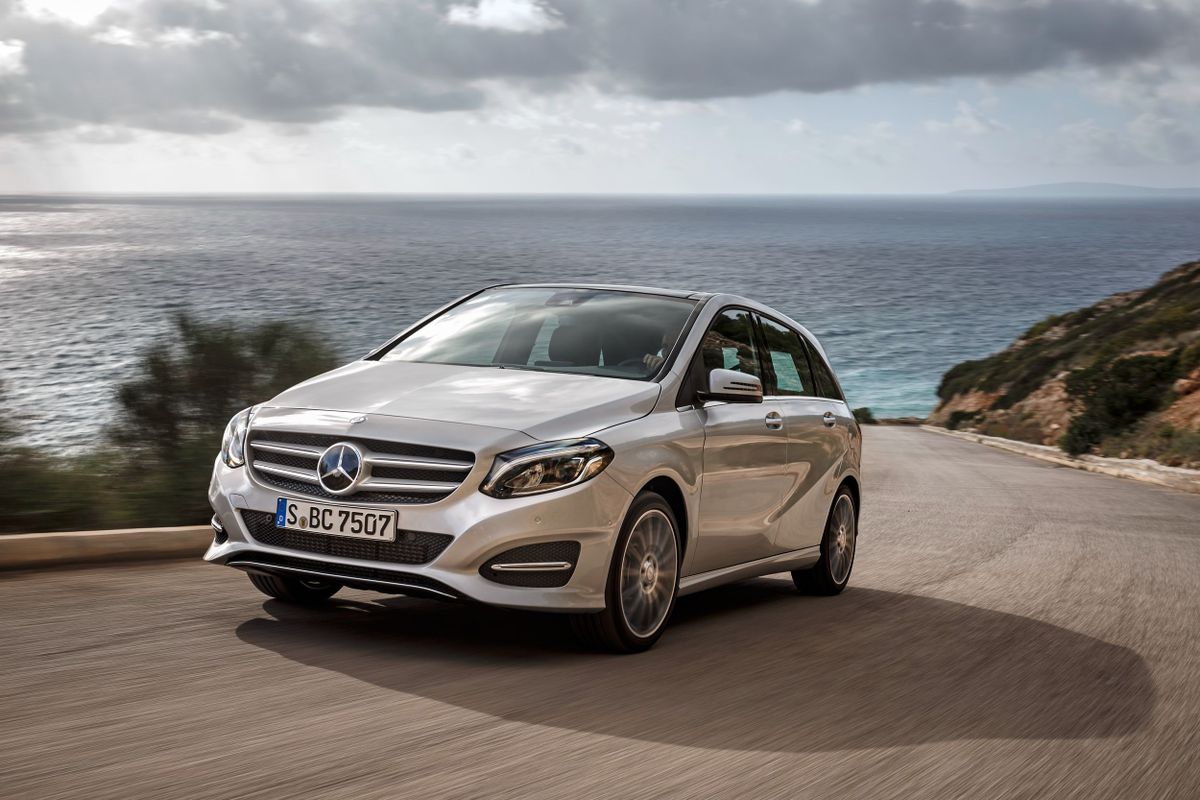
Mercedes-Benz positioned the W246 as a sports touring car that combined a roomy interior with the dynamic performance of a hatchback sedan, and tried to express this in its design. ‘Sportiness’ was emphasized by a particular side line with the hood smoothly passing into the rack, and the roof line smoothly descending to the roof spoiler. The vehicle acquired massive wheel arches, whereas the lower edge of the body was ‘decorated’ with dynamic side plates.
But what’s important is that the engineers managed to reduce the drag coefficient to 0.26, approaching the parameters of the E-Class Mercedes, which was a kind of sensation. At the same time, the developers solved a controversial task by increasing the height of the B-Class to 1,557 mm and lowering the fit by 5 cm compared to the first generation. The seating height in relation to the road was also reduced (minus 86 mm to the first generation). The base W246 model was 4,359 mm long and 1,786 mm wide.
The drag coefficient of the second generation Mercedes B-Class was 0.26, which was close to that of the E-Class models. During development, it was necessary to simultaneously lower the fit and increase the height of the vehicle.
Engines and chassis
The second generation B-Class vehicles could be equipped with the BlueDIRECT six- and eight-cylinder engines. The base engines were the 1.6-liter four-cylinder engines, the B 180 with 90 kW (122 hp) and the B 200 with 115 kW (156 hp). The W246 could also be equipped with a new 1.8-liter four-cylinder diesel engine, which was an upgraded OM651 used on the third generation C- and S-Class models, featuring the common rail direct injection technology. The B 180 CDI developed 80 kW (109 hp), while the B 200 CDI developed 100 kW (136 hp). The W246 came with a 7G-DCT dual-clutch transmission or a new 6-speed manual transmission.
The developers tried to improve the dynamic performance of the second generation B-Class with the help of a 20 mm lower center of gravity, a new four-link rear axle and an upgraded ESP. The suspension was additionally equipped with sports shock absorbers with amplitude-selective damping and direct steering.
Safety
The second generation B-Class vehicles were the first compact cars to be fitted as standard with radar collision avoidance systems in conjunction with adaptive emergency braking. The system visually and audibly warned the distracted driver about an obstacle and at the same time prepared the emergency braking system for the most accurate response to braking when the ‘awakened’ driver sharply pressed the brake pedal.
Moreover, this vehicle was first in the class to feature the PRE-SAFE preventive passenger protection system, which provided reversible belt tension, closed side windows and a sliding sunroof, and brought the front passenger’s seat to an optimal state in case of critical dynamics. The W246 was standardly equipped with tensioners, tension limiters and belt height adjusters. The built-in child seats were borrowed from the previous generation.
Interior
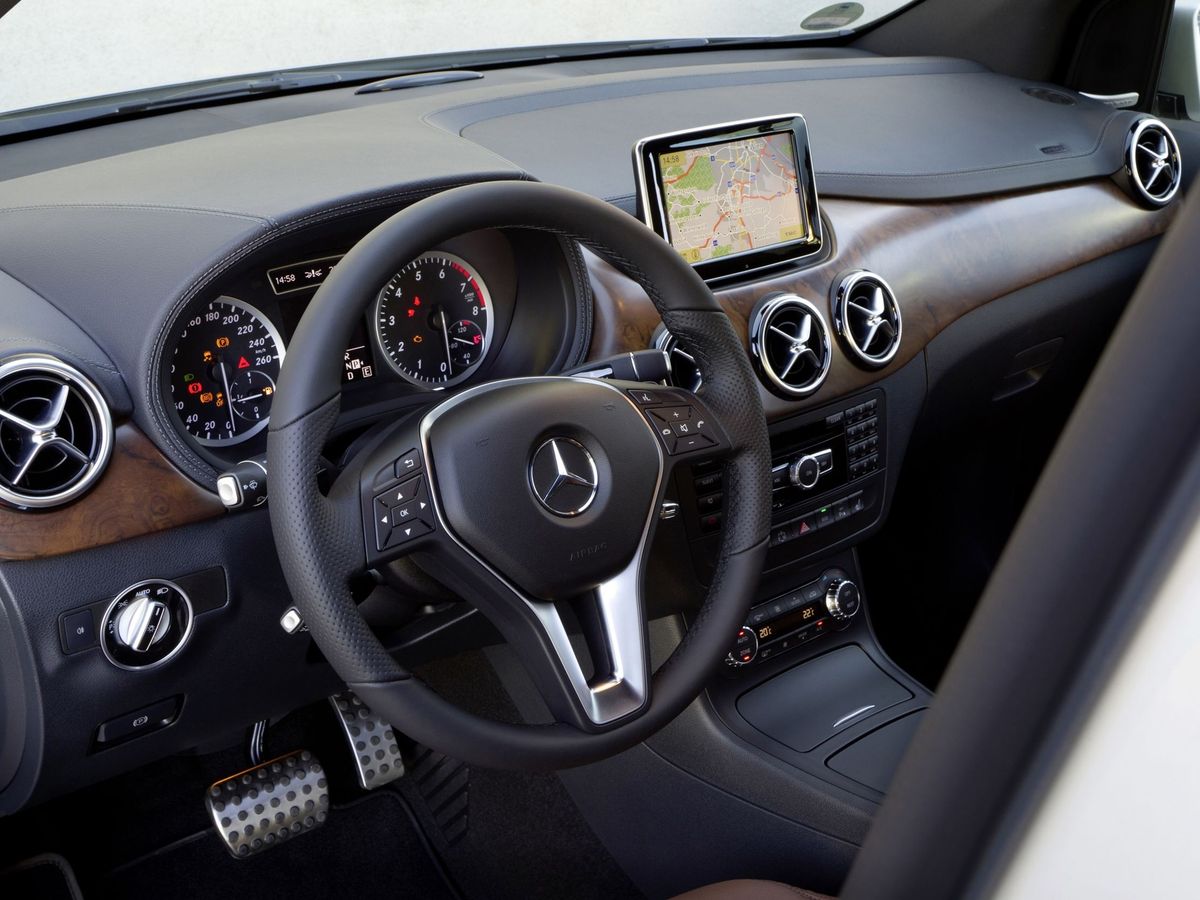
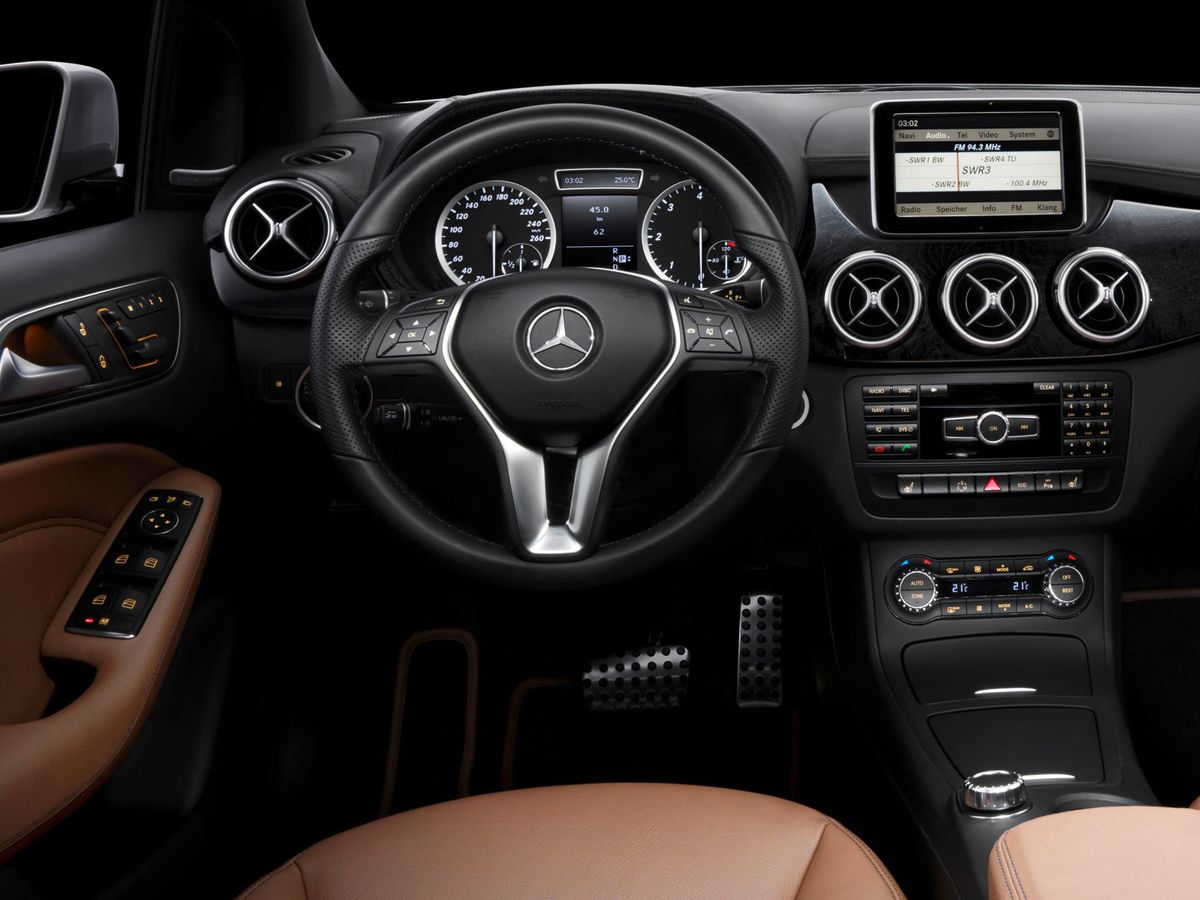
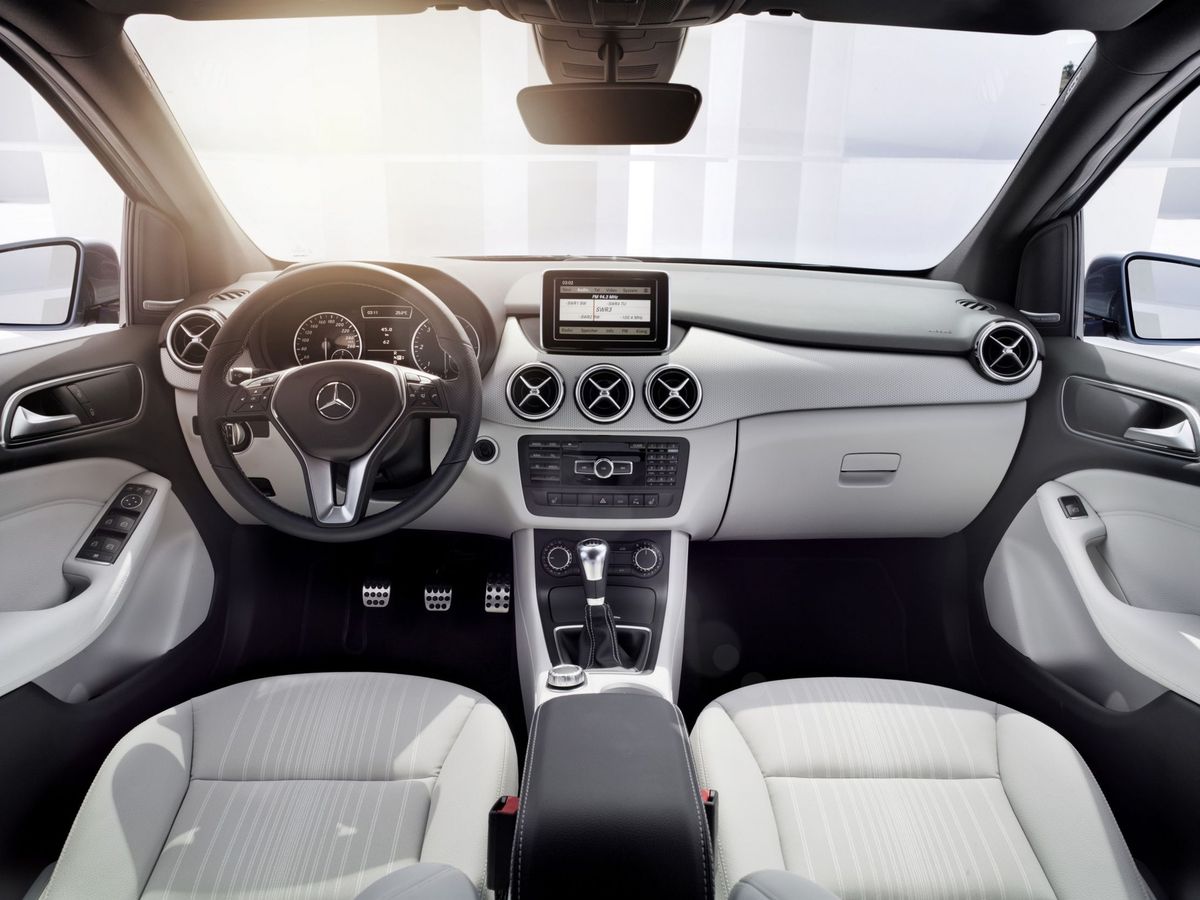
With a maximum nose height of 1,047 mm (without a sliding roof), the B-Class was one of the most spacious vehicles in its segment. The lowered seat was installed more ergonomically, which, combined with the lowered rear floor of the vehicle, resulted in increased legroom (976 mm), even more than in the S- and E-Classes. It should be noted that the second generation of the B-Class could optionally be equipped with the EASY-VARIO-PLUS system, which allowed reorganizing the space for transporting large and complex items. The system adjusted the position of the rear seats and the passenger space so that the volume of the trunk compartment increased from the standard 488 to 666 liters.
The second generation of the B-Class retained a sufficient amount of multimedia devices. The vehicle featured an innovative design of the infotainment system screen, which was located at the top of the dashboard. The screen itself was not yet touch-sensitive, but multifunctional. The COMAND Online multimedia system had Internet access, a LINGUATRONIC voice control system, a navigation interface, and the ability to connect mobile audio devices. Google Local Search and Weather services were integrated into the Internet application, as well as the ability to download a traffic route using Google Maps.
2014 restyling
The restyled B-Class W246 was introduced on November 22, 2014. The exterior and interior changed slightly. Thus, the vehicle featured a bumper with new large air intakes, headlights with LED daytime running lights and exhaust linings integrated into the rear bumper. But all vehicles were brought into compliance with Euro 6 emission standards, with the exception of the diesel B 180 CDI BlueEFFICIENCY Edition. As a result of improvements, the engines became more efficient and environmentally friendly. During the restyling, the second generation was divided into three versions:
- Style: A model with a progressive design, for example, it had a radiator grille with chrome inserts, as well as with chrome bumper elements, 16-inch 10-spoke alloy wheels, etc.
- Urban: In addition to the same chrome trim, the model featured a twin-pipe exhaust system integrated into the bumper, a multifunctional leather-trimmed steering wheel, a modified instrument cluster and so on.
- AMG Line: There were front, side and rear pads typical for Mercedes AMG models, 18-inch AMG alloy wheels, a sports suspension with a lowered body and direct steering, sports pedals.
Modifications
The second generation of the B-Class offered a model that ran on natural gas. In 2013, the company launched a car with a gas-adapted B 250 engine. The B 200 Natural Gas Drive was powered by one large and two small natural gas tanks located in the floor under the rear seat and provided a drive range of 500 km.
In mid-2014, Mercedes offered an electric vehicle with an adapted Tesla Model S front engine, an 11 kW three-phase charger and a 28 kWh battery pack. In urban mode, the design drive range was 200 km, but in reality it turned out to be no more than 150 km. Unlike the Tesla Model S, the electric B-Class did not have a dual on-board charger and quick charge option, so it was quickly discontinued.
Sales
Consumers liked the second generation of the Mercedes B-Class. From November 2011 to June 2012, sales in Europe exceeded 70 thousand units. Throughout 2012, 145.6 thousand units were sold in the world. This exceeded the estimated demand and was the highest indicator for the B-Class since 2005.
And yet, the second generation of the B-Class is not exactly a great success for Mercedes-Benz. The most popular were the B 180 and B 180 CDI diesel models with navigation system. That is, buyers preferred economy-type cars without sports gadgets. In this form, the second generation of the B-Class lasted until 2018, which is a very good result.