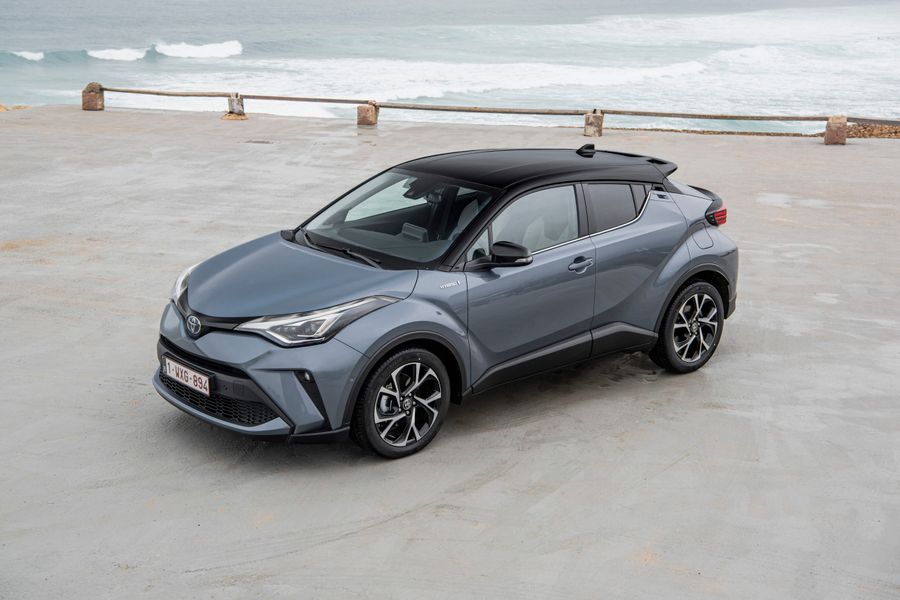
Toyota Prius Plug-In hybrid. Charge and get charged
Toyota Prius Plug-In is a front-wheel-drive hybrid passenger car produced by Japanese automaker Toyota since 2015. It has a liftback body and belongs to the M class. The Prius Plug-In is an option of the basic Toyota Prius model with an enlarged battery pack that can be recharged from an external power grid. The updated version of the Toyota Prius Plug-In was unveiled in 2017 and is available on the today’s Israeli market.
For its eco-friendliness, low emissions, and low fuel consumption, the Prius has won many prizes and awards, being recognized as the ‘Car of the Year’ in Japan, North America, and EU.
First generation
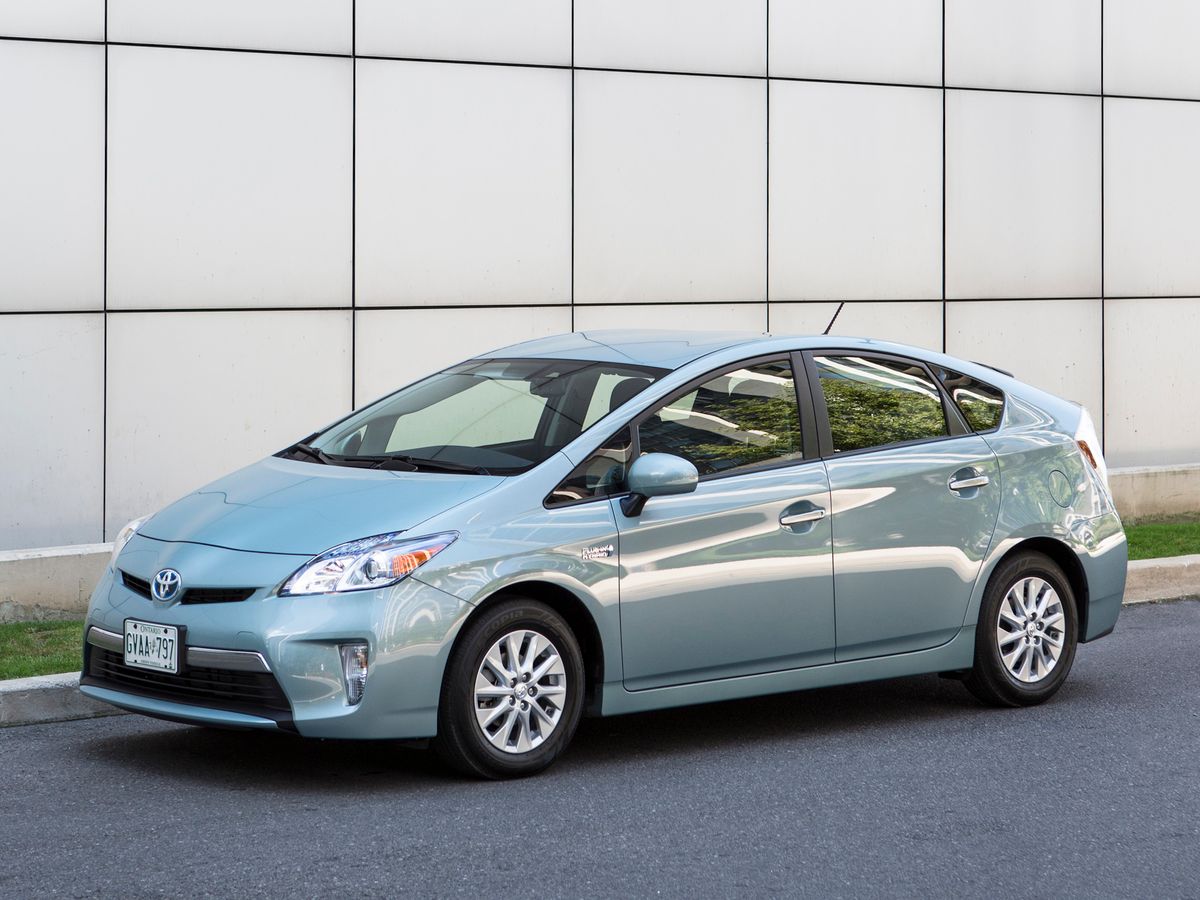
The first Prius Plug-In or Prius PHV with plug-in charging capability appeared in 2012 as a third-generation Toyota Prius. In North America, the Prius Plug-In has been sold as Prius Prime. The electric mode is used for short trips across the city, while the internal combustion engine is used for long out-of-town trips. According to the manufacturer, the Prius Plug-In has the right balance between mileage, charging time, battery size, and cost. The first-generation Prius Plug-In could only drive about 25 kilometers on electric power at 80 km/h or less. The longer range made it more fuel efficient, consuming about 45% less fuel than the base Prius. Externally, the first Prius Plug-In did not look much different from the base model, and inside, five adults were seated in the same comfort as in a conventional Prius. Mass production of the first Prius PHV lasted until June 2015. About 100,000 first-generation Prius Plug-In plug-in hybrids were sold worldwide.
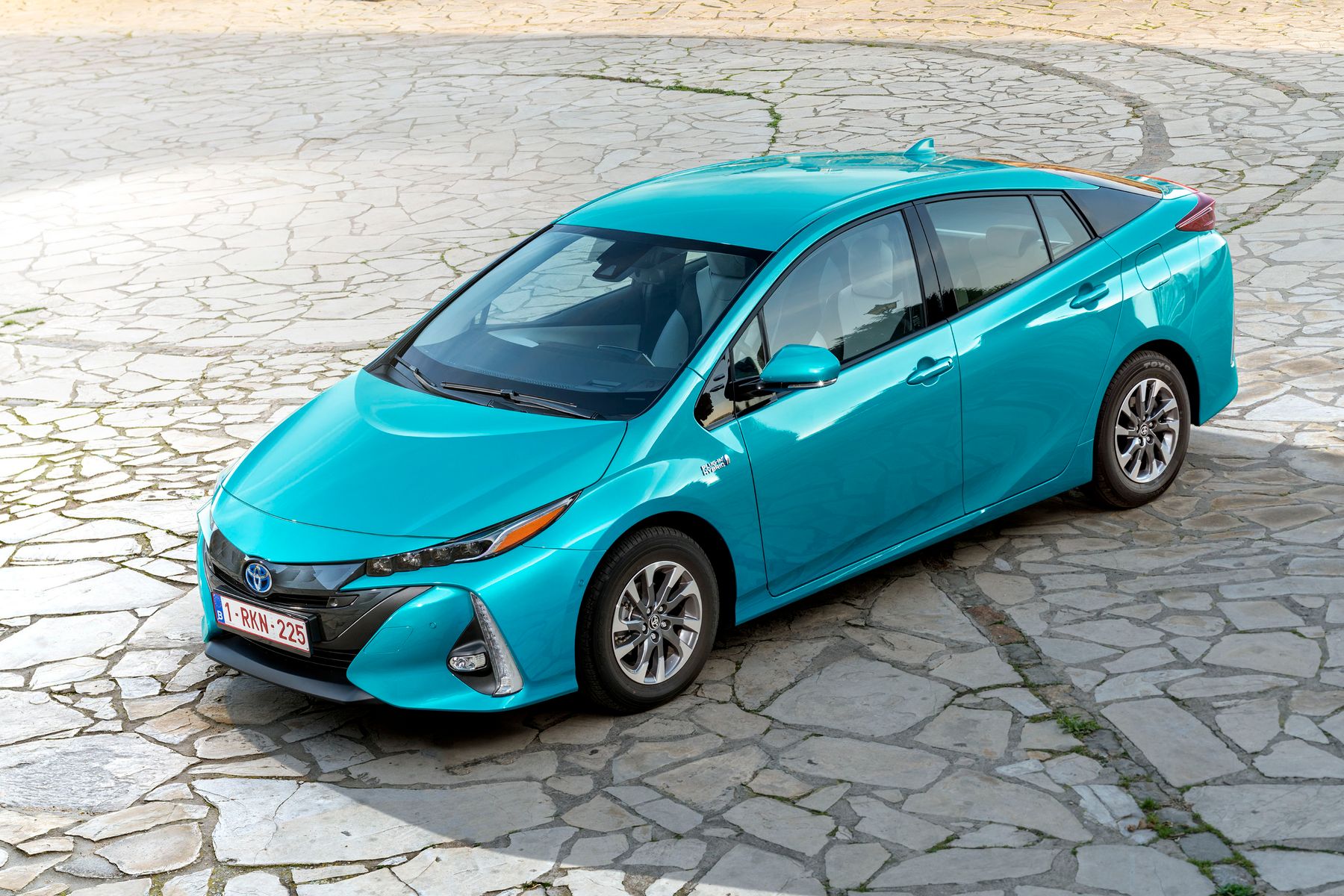
Second generation
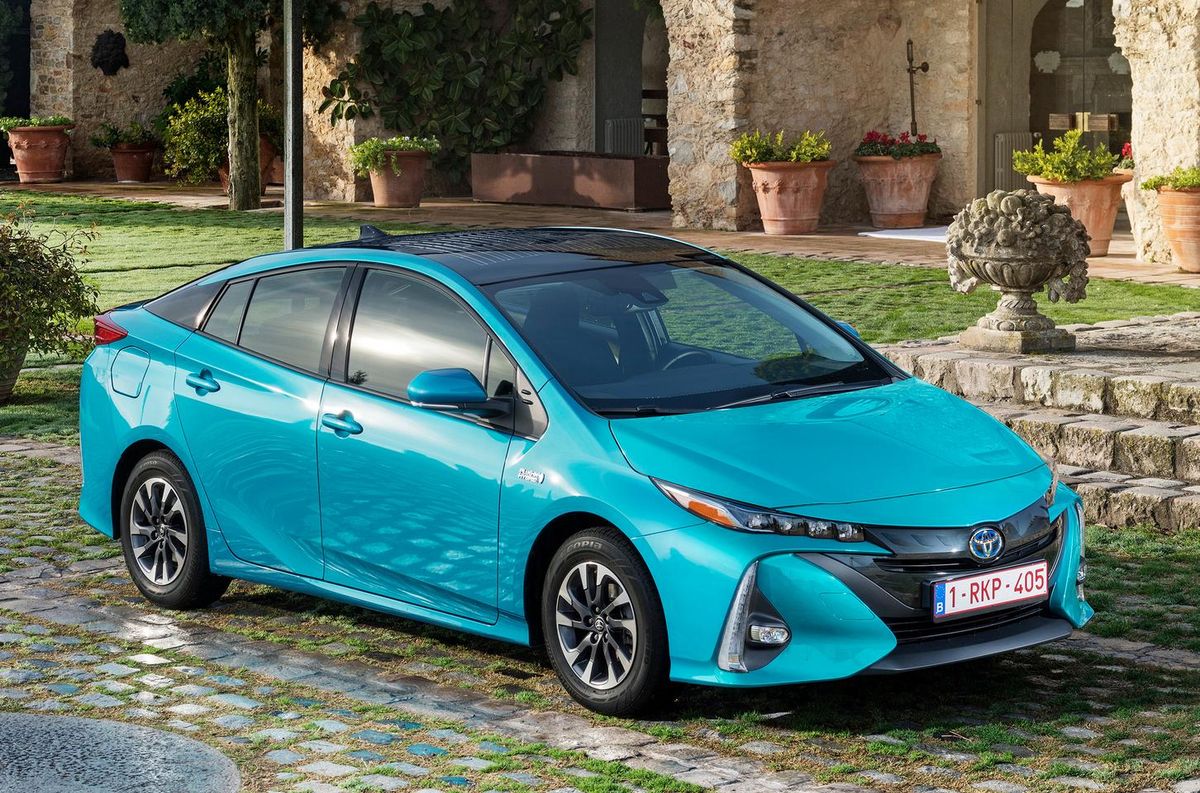
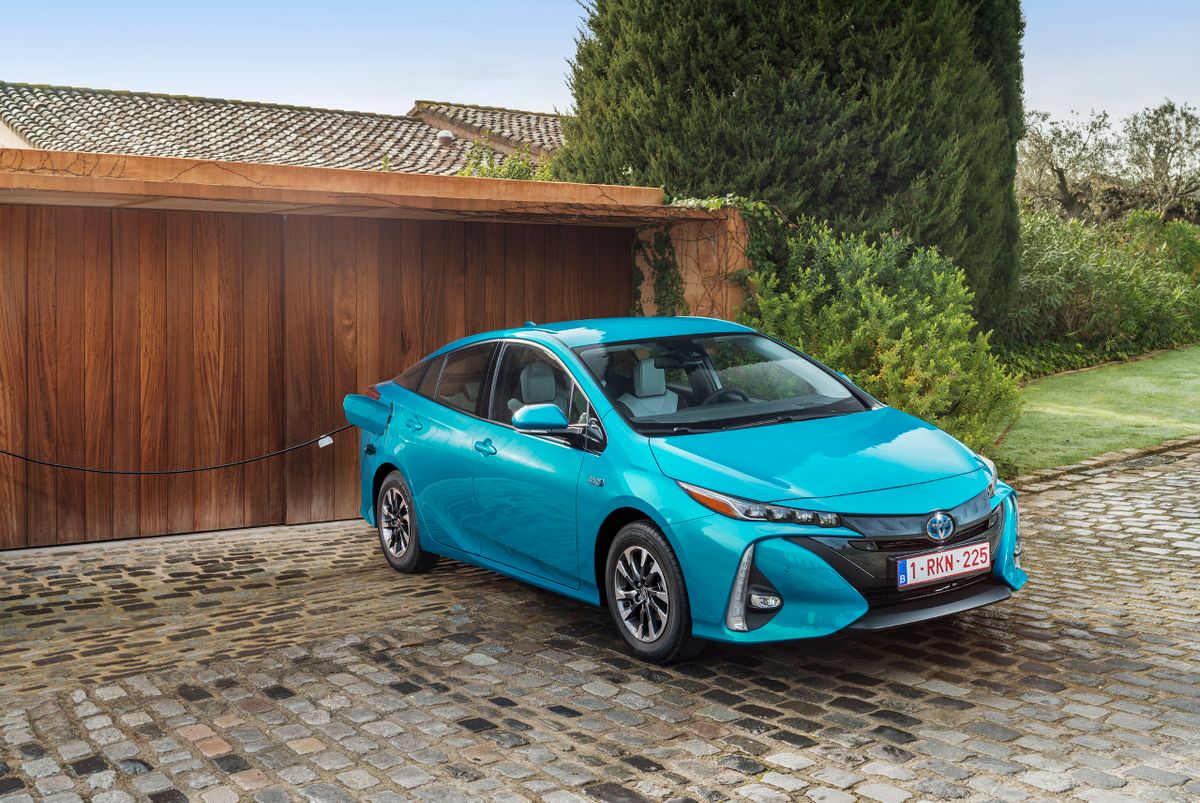
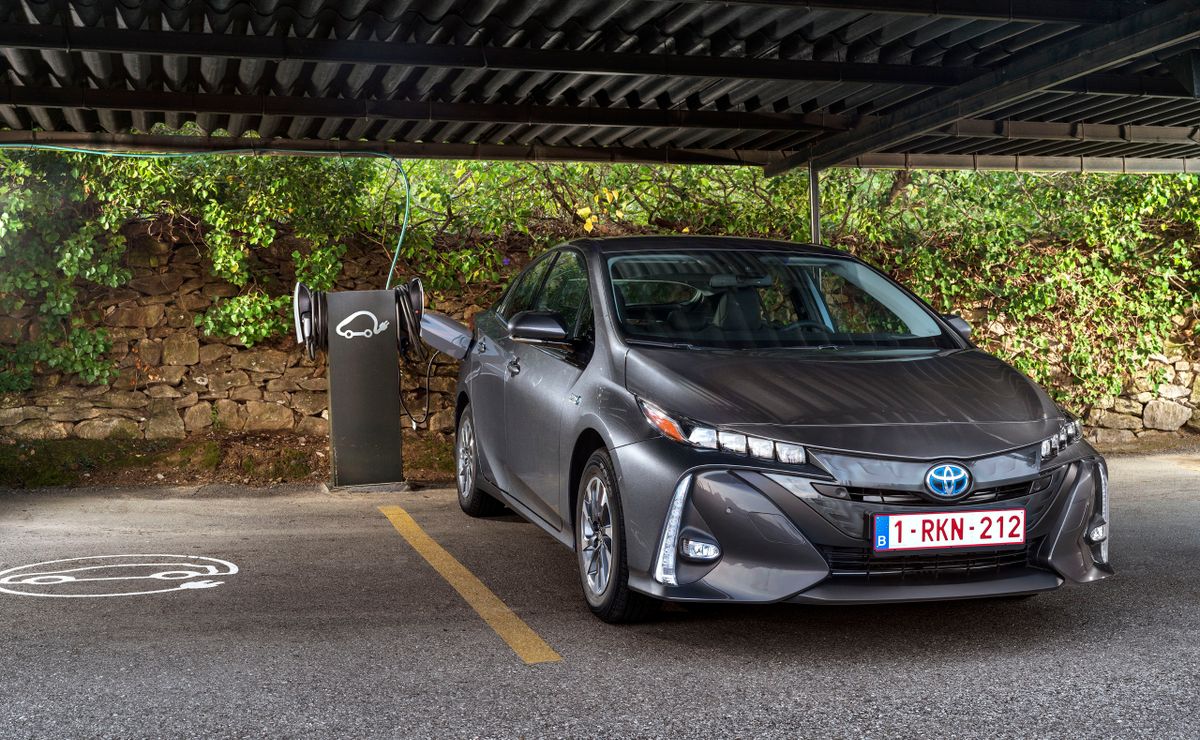
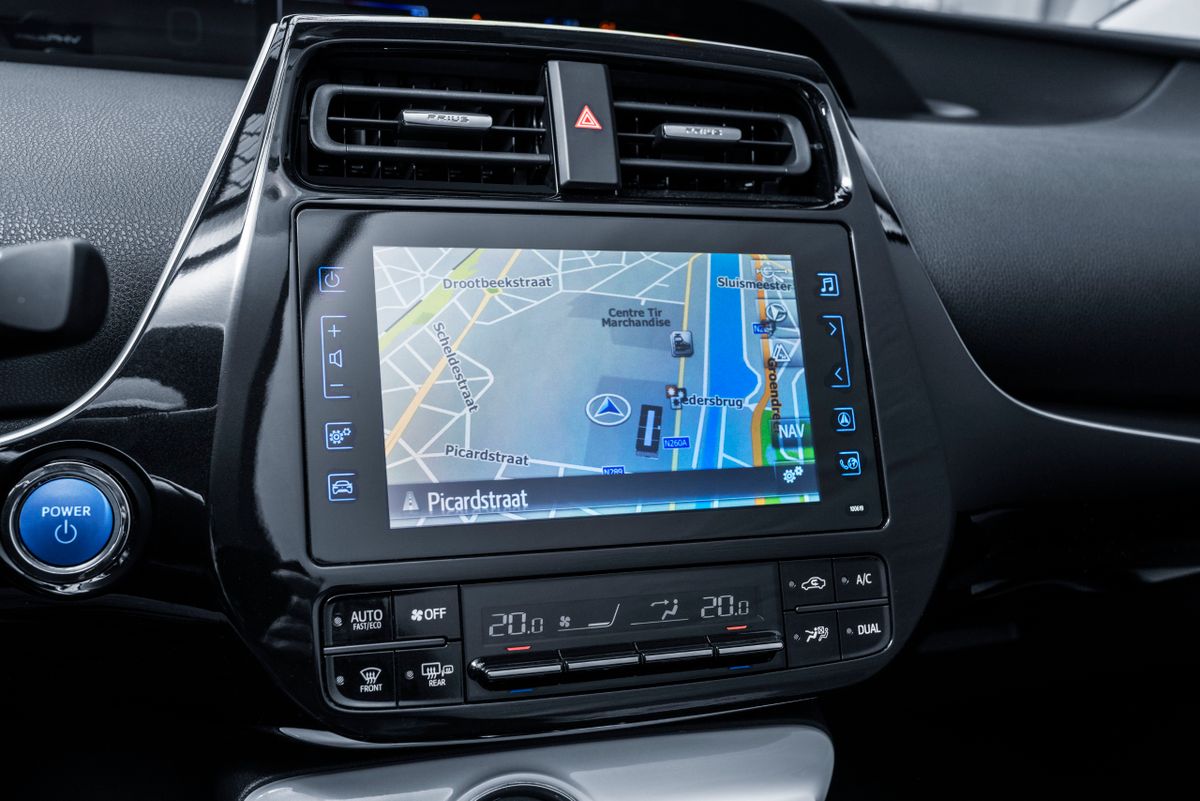
The second-generation Prius Plug-In appeared in February 2017. It was based on the fourth-generation Toyota Prius. The new Plug-In liftback has a slightly different front and rear design than the base Prius. The new battery of the second-generation Plug-In has an increased capacity and allows it to drive up to 68 kilometers in electric mode at speeds of up to 135 km/h. It can be recharged to 80% of its maximum in just 20 minutes at a quick-charge station. The time to fully charge the car from the home electrical grid is from 2 to 14 hours, depending on the voltage and allowable current strength.
The new Toyota Prius Plug-In can be used as a source to power appliances in the countryside or emergency areas. Fully charged and with a charged battery, it can output 40 kWh for four days.
The new Prius Plug-In differs from the basic Prius in exterior. It has a different design of the front end. Large, voluminous elements form the grille and bumper tips, with vertical daytime running lights and ultra-compact LED headlight units on top of the fenders. The 2017/2018 Prius Plug-In has a longer rear end, a lower spoiler and new two-tone wheels. The tailgate is made of carbon fiber, with a concave glass that follows the shape of the spoiler, 40% lighter than a similar aluminum door.
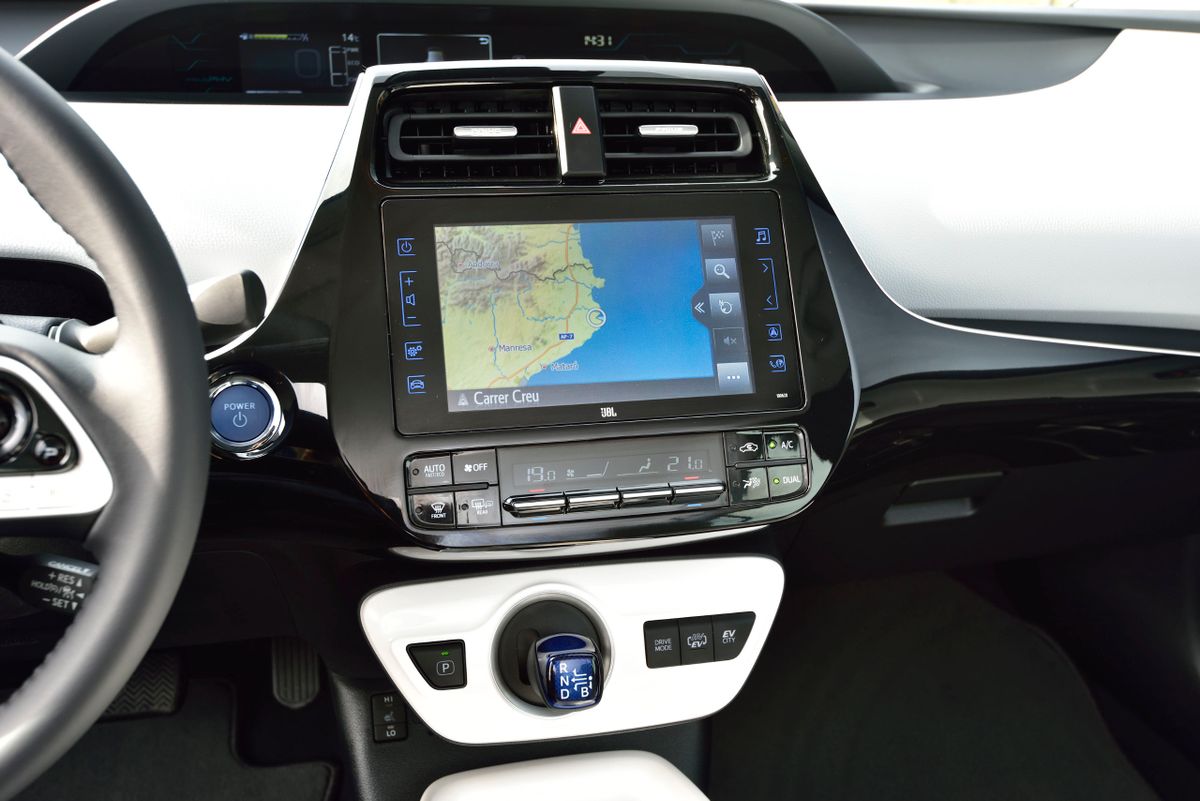
The interior of the 2019 Prius Plug-In has not changed much, the rear seat is now two seats with separate seats and a console between them. Because of the large battery, the floor in the trunk has been raised by 160 millimeters, which reduced its volume to 360 liters. Instead of a spare tire, the trunk holds a set to repair a punctured tire, the same as in the previous generation Plug-In model. Good handling of the car is provided by specially tuned suspension. It uses special front and rear springs and shock absorbers and a more powerful stabilizer bar at the rear.
The new Toyota Prius Plug-In can be used as a source to power appliances in the countryside or emergency areas. Fully charged and with a charged battery, it can output 40 kWh for four days.